Karnataka State Syllabus Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
KSEEB Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give an example of a metal which
Answer:
Mercury
ii) Can be easily cut with a knife
Answer:
Sodium
Answer:
Silver
iv) Is a poor conductor of heat
Answer:
Lead
Question 2.
Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile?
Answer:
- Malleable: Some metals can be beaten into thin sheets. This property is called Malleability.
- Ductility: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires is called ductility.
Question 3.
Why is sodium kept immersed in Kerosene oil?
Answer:
Sodium is a very reactive metal. It reacts vigorously with the water and oxygen present in air and even catches fire. Hence, to protect sodium, it is kept immersed in Kerosene oil.
Question 4.
Write equations for the reactions of
(a) Iron with stream
(b) Calcium and potassium with water.
Answer:
(a) 3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g)
(b) Ca(s) + 2 H2O (I) → Ca (OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2(g)
Question 5.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.
Use the table below to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
| Metal | Iron (II) Sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | …………. | …………….. |
| B | Displacement | ……………… | No reaction | ………………. |
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
(i) Which is the most reactive metal?
Answer:
B is most reactive
(ii) What would you observe, if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
Answer:
B will displace copper from copper (II) sulphate.
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity
Answer:
B > A > C > D
Question 6.
Which gas is produced, when dilute HCL is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical equation, when iron reacts with dil. H2SO4?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is produced when a metal reacts with HCl.

Question 7.
What would you observe, when Zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
When zinc is added to a solution of iron II sulphate, the greenish colour of iron II sulphate solution fades away gradually, due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution Iron metal is deposited on zinc.

Question 8.
i) Write the electron dot structures of sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electors.
iii) What are the ions present in these compounds
Answer:
(i)

(ii) Formation of Na2O: The atomic number of sodium is 11 and it has only one valence electron. Hence electronic configuration of Na11 is 2,8,1. The atomic no of oxygen is 8 and it has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Hence electronic configuration of O8 is 2,6.
Sodium has a tendency to lose the valence electron and oxygen has a tendency to gain the electron lost by sodium. Since, sodium can lose only one electron of the valence shell and oxygen atom needs two electrons to complete its octet in the valence shell, two atoms of sodium combine with one atom of oxygen. By losing valence electron, sodium is changed into Na+ and by gaining two electrons lost by two sodium atoms, oxygen atom is changed into an oxide anion.
O2-. In this process both the atoms, sodium and oxygen obtain the stable electronic configuration of Neon.

The oppositely charged sodium ion, Na+ and oxide ion, O2- are now held together by electrostatic forces of attraction or electron valent bond, Na2O is, therefore, an ionic or electron valent compound.
Formation of MgO:
The atomic number of magnesium =12.
Its electronic configuration is K = 2, L = 8, M = 2.
It has two electrons in its outermost shell. So, the magnesium atom donates its 2 valence e’ns and forms a stable magnesium ion Mg2+, to attain the electronic arrangement of neon gas.

The atomic number of oxygen = 8 Electronic configuration ⇒ K = 2, L = 6
It has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Therefore it requires two more electrons to attain the stable electronic arrangement of neon gas. Thus oxygen accepts two electrons donated by magnesium atom and forms a stable ion O2-
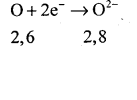
The oppositely charged magnesium ions, Mg2+ and oxide ions, O2_ are held together by a strong force of electrostatic attraction. form magnesium oxide compound Mg2+ O2- or MgO.
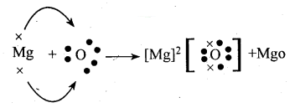
MgO is an ionic compound.